What is a site plan?
A site plan for an industrial project is a detailed and comprehensive document prepared by the design consultants that details the layout, arrangement, land utilization, placement of structures and buildings within a specific industrial facility or project site.
It is a visual representation of the physical layout of the project. This is a integral part of the project documentation and used by the project stakeholders including architects, engineers, project managers, and construction teams. In case of an expansion project, the site plan provides for the existing and proposed expansion details. However, the site plan must show the relation between the existing and the proposed addition.
Components of a site plan
The key components of an industrial project site plan include:
- Drawing Details: Title block, legends, project name, drawing number, scale, revision number, directional orientation, area allocation.
- Boundaries: The site plan defines the boundaries of the project site, including property lines and neighboring structures or facilities.
- Topography: This plan also provides information about the existing topography and terrain of the site, including elevations, slopes, and any grading plans to ensure proper drainage.
- Access: The site plans shows access points, roads, driveways, parking area for the project.
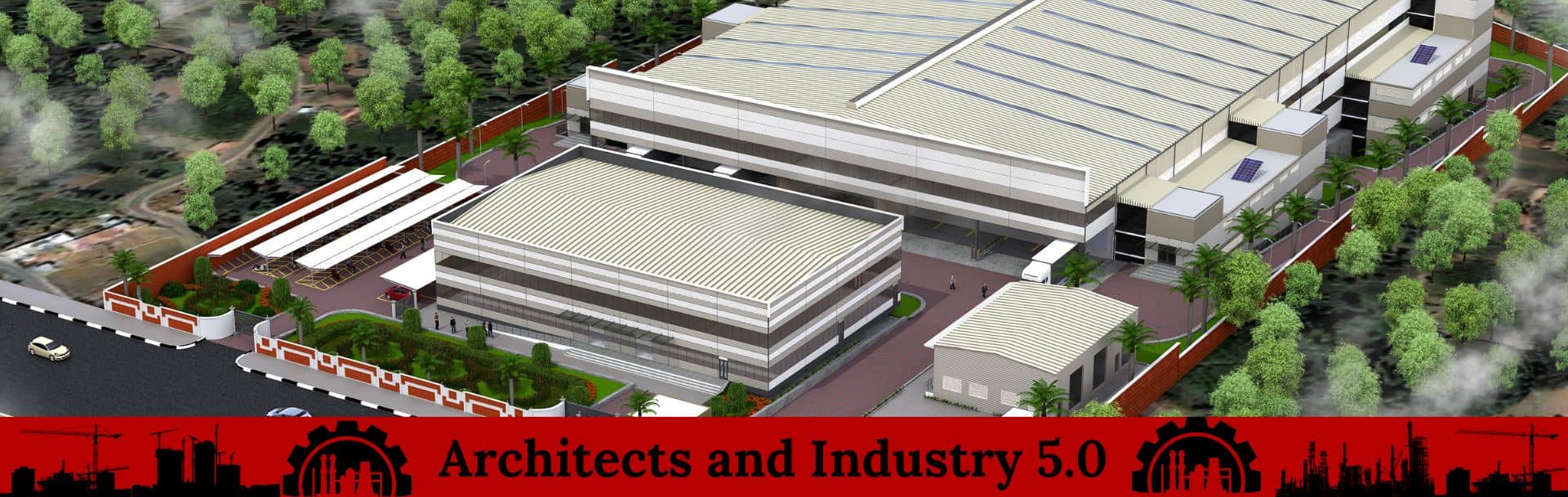
- Building Footprints: The site plan indicates the location, size, and orientation of buildings within the industrial facility. This includes manufacturing facilities, warehouses, administrative buildings, and other structures.
- Utility Infrastructure: This site plan also provides for the placement of utilities such as water supply, sewage systems, electrical lines, gas lines, and other essential infrastructure.
- Outdoor Spaces: Allocation of outdoor spaces, including storage yards, loading docks, and any open areas required for specific industrial activities are also marked on the site plan.
- Landscaping: The site plan also demarcates the areas for landscaping elements, green spaces, and buffer zones, which may be necessary for environmental, aesthetic, or regulatory reasons.
- Security Measures: The site plan mentions the security features such as fences, gates, security checkpoints, and surveillance systems.
- Emergency Response: Identification of emergency response features, such as access roads for emergency vehicles and the location of emergency exits.
- Environmental Considerations: Typically, a site plan also mentions the environmentally sensitive areas, conservation measures, or mitigation strategies required for compliance with environmental regulations.
- Zoning and Land Use Compliance: Architects ensure that the site plan aligns with local zoning regulations and land use requirements.
- Site Amenities: Site amenities like employee amenities, such as break areas, cafeterias, and recreational facilities also are mentioned on the site plan.
A well-designed industrial site plan takes into account safety, efficiency, and compliance with relevant regulations. It serves as a guide for the project stakeholders, helping them understand the spatial relationships between different elements of the project. Additionally, it aids in obtaining necessary permits and approvals from regulatory authorities. The site plan is an integral part of the overall project documentation and plays a crucial role in the successful execution of industrial projects.
Importance of a site plan in industrial projects
A site plan is critical in most industrial projects for several reasons. Additionally, it serves as a detailed & visual representation of the project site. Moreover, it provides essential information for planning, design, construction, and regulatory compliance. Some key reasons why a site plan is crucial for industrial projects are:
- Spatial Layout: A site plan provides the spatial organization of the industrial facility, including the layout of buildings, infrastructure, and outdoor spaces. This helps ensure efficient use of space, proper flow of materials, and optimal placement of equipment and structures.
- Infrastructure Planning: The plan identifies and locates critical infrastructure components such as utilities, roads, drainage systems, and parking areas. Proper infrastructure planning is essential for the functionality and safety of the industrial facility.
- Regulatory Compliance: Industrial projects are subject to various zoning regulations, environmental guidelines, and safety standards. A site plan helps demonstrate compliance with these regulations. Moreover, it is a crucial document for obtaining permits and approvals from regulatory authorities.
- Environmental Considerations: Site plans take into account environmental factors, such as the location of water bodies, wetlands, or protected areas. They may include measures for environmental protection and mitigation of potential impacts.
- Safety and Emergency Planning: The plan can include details related to safety features, emergency exits, fire lanes, and other elements. Thus, it is critical for the safety of workers and emergency response teams.
- Logistics and Traffic Flow: For industrial projects involving the movement of goods and materials, a site plan helps optimize logistics and traffic flow. It ensures that there are efficient routes for transportation within the site.
- Utilities and Services: The plan indicates the placement of utility connections, including water supply, sewage systems, electrical lines, and gas lines. This information is crucial for the efficient functioning of the industrial facility.
- Project Communication: A site plan is a valuable communication tool among various stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, investors, and regulatory authorities. It provides a visual reference that helps convey the project’s design intent and layout.
- Construction Planning: During the construction phase, the site plan guides the PMC team in implementing the project. Moreover, it helps contractors understand the location of structures, grading requirements, and the sequence of construction activities.
- Cost Management: A well-developed site plan contributes to effective cost management by ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. It helps prevent costly mistakes and changes during the construction process.
- Future Expansion: If there are plans for future expansion, the site plan can include provisions for scalability. So, the site plan ensures that the current project layout allows for future growth without significant disruptions.
Conclusion
In summary, a site plan is integral to the success of industrial projects. It provides a comprehensive and organized view of the project site. Additionally, it aids in regulatory compliance, safety planning, efficient use of space, and effective communication among stakeholders. To conclude, this document influences the entire project lifecycle, from planning and design to construction and completion.